High Power

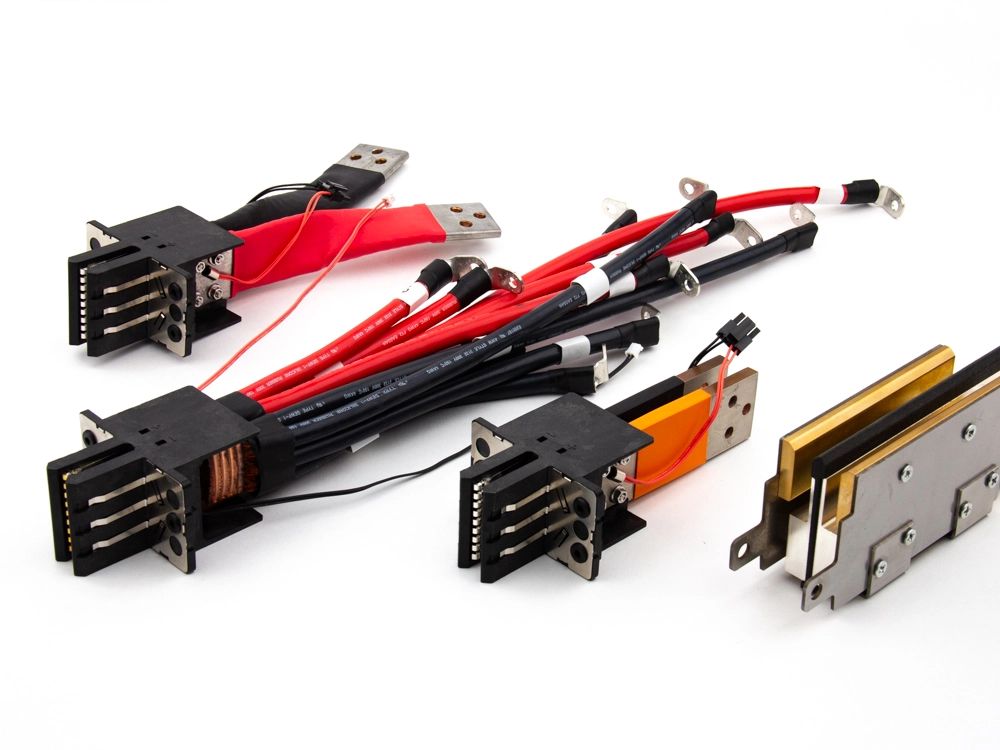
Busbar Clip Power Up to 300Amp
300Amp 9192-B Series 200Amp 9192-A Series 180Amp 9192 Series 30Amp 9192-D Series 16Amp 9192-A Series Busbar Conductor 9192 Series
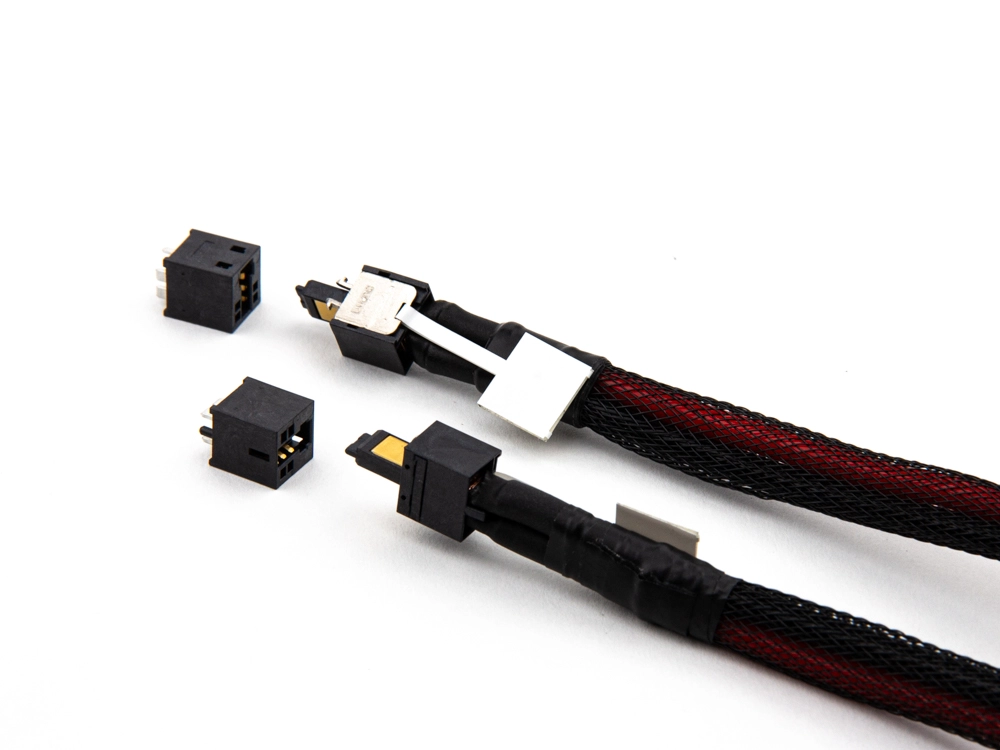
High Power BTB Connectors 65AMP to 150AMP
150Amp High Current Type D 9113-D+9114-D Series 100Amp PwrFULL® High-Performance Power 9311 Series 100Amp High Current Power 9310 Series 100A/65A PwrSword® Ultra HD+ 9303-D Series 90Amp Blade Type Power 9397 Series 75A(DC)/45A(AC) PwrSword® Ultra HD 9303-C Series 75Amp High Flow Power HFP® 9113-E+9114-E Series 65Amp PwrSword® + Connector 9303 Series
High Power BTB Connectors 15AMP to 60AMP
60Amp Max P60™ 9395 Series 60Amp High Flow Power HFP® 9113-F+9114-F Series 45Amp High Flow Power HFP® 9113+9114 Series 30Amp PwrSword® Connector 9391-A Series 20Amp HVDCP® 9113-C+9114-C Series 20Amp Rapid Power connector 9113+9114 Series 15Amp Power Pin 4191 Series
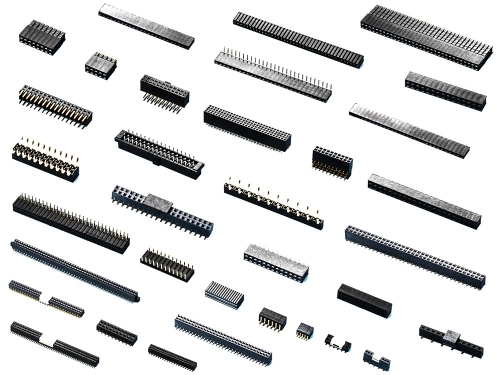
High Speed
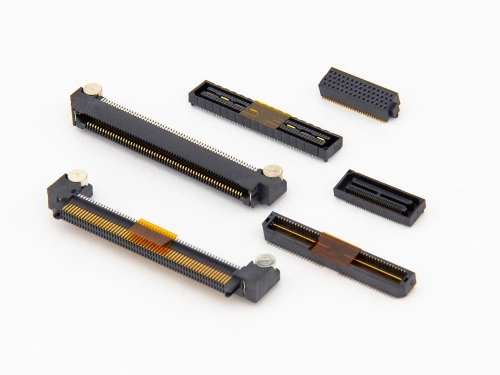

BackPlane
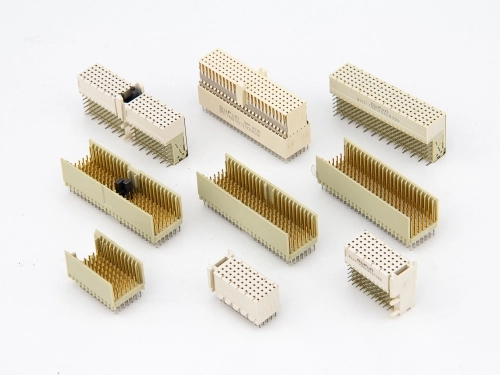
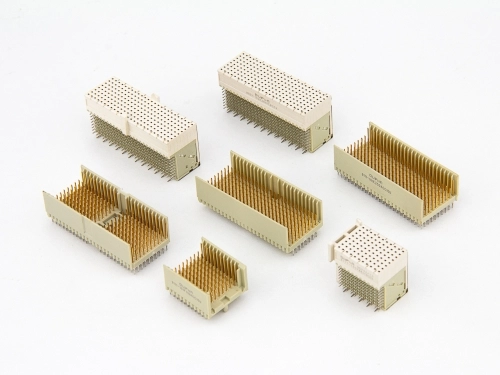

Hard Metric Type L to N, Others
Hard Metric Type L 9111-7 Series Hard Metric Type M 9111-7 Series Hard Metric Type N 9111-7 Series Coding 9111 Series Power Modules 9111-3 Series Hard Metric Shroud 9111-7 Series
Automotive, I/O
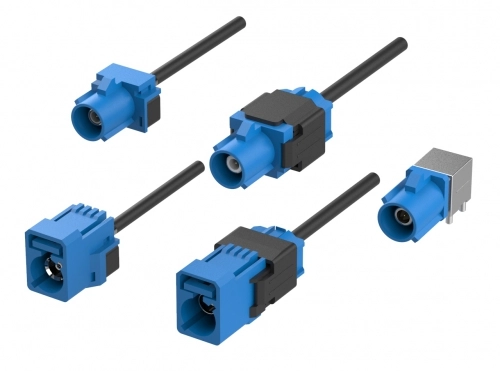

Board to Board




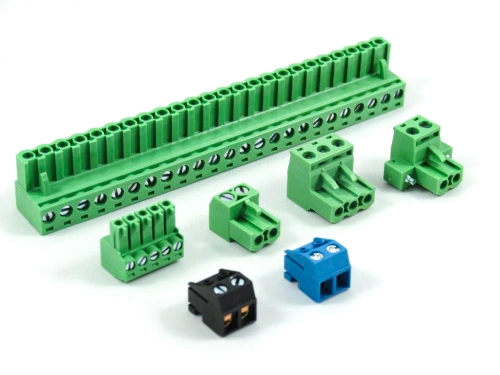
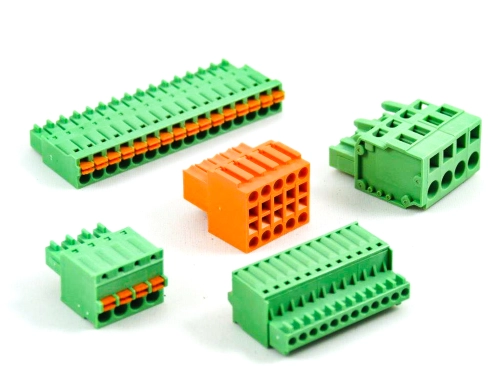
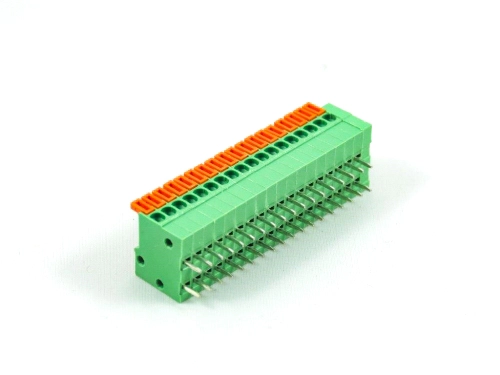
Terminal Blocks


Fixed Type Rising Clamp PCB Mount
3.50mm 8932-C Series 5.00mm 8932-F Series 5.08mm 8932-G Series 6.35mm 8932-H Series 7.50mm 8932-I Series 7.62mm 8932-J Series 9.52mm 8932-V Series
Cables,Wires,Others

Connectors, IDC Cable Assembly
IDC Socket 1001 1101 1203 1204 Series IDC Plug 3016-A 3017-A Series Micro Match 6022 Series Transition Plug 6111 6211 Series Flat Cable FC FC1 FC4 Series Cable Assembly
Wire To Board Connectors 0.80mm to 2.54mm
0.8mm 4876 Series 1.0mm 4472 4473 Series 1.25mm 4573 4574 4575 Series 1.5mm 4572 Series 1.8mm 4190 Series 2.0mm 4172 Series 2.5mm 4671 Series 2.54mm 4071 4072 4073 4074 4077 Series
ENG